Women's Health
Discover exceptional care for women’s health concerns at PIIT, with a focus on innovation and advanced technology, we offer modern treatment options to address various women’s health issues. From Uterine Fibroid Embolization to Varicose Vein treatment, our expert interventional radiologists deliver compassionate care with precision and expertise. Explore our range of cutting-edge solutions and take control of your health journey with us!
Varicose Vein treatment
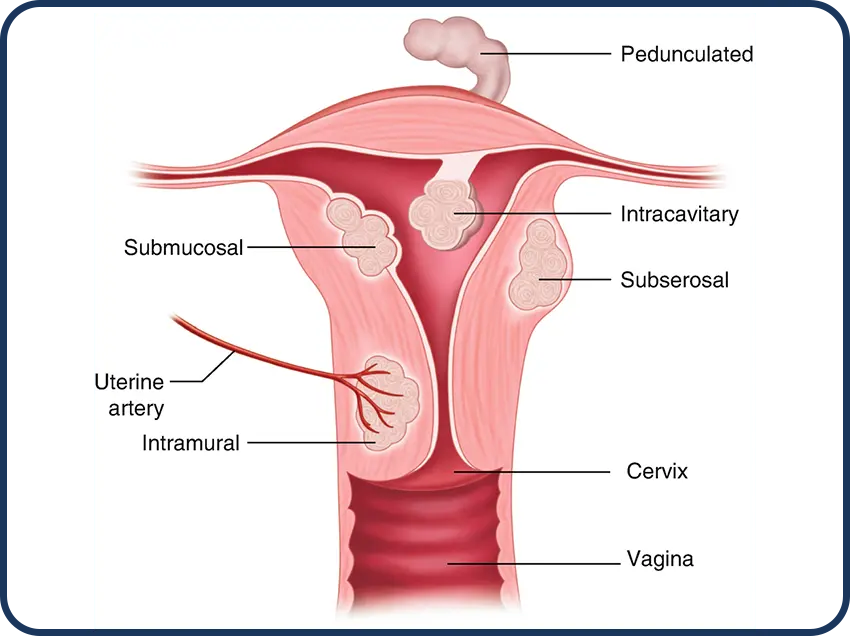
Varicose Veins are a condition of Vascular malformations also known as Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)
Vascular malformations are abnormal clusters of blood vessels that can vary in appearance and severity. Some may resemble birthmarks and are present from birth, while others may develop over time and cause pain, swelling, or changes in appearance. Treatment options for vascular malformations depend on their type and location.
Minimally invasive treatments for abnormal tangles of blood vessels are available at PIIT. These procedures involve blocking the abnormal blood vessels to induce their collapse and shrinkage. Two common treatments are AVM Embolization and Sclerotherapy. These procedures aim to block off or destroy the abnormal vessels, respectively.
Sclerotherapy
The procedure begins with the doctor prepping your wrist or thigh area with antiseptic solution some local anesthetic will be injected. This may sting briefly before going numb.
Why is this procedure recommended?
This procedure is recommended in the following cases:
- To improve the cosmetic appearance.
- To reduce symptoms such as pain and buming.
How is this procedure performed?
- Your doctor will prepare the area where the needle is to be inserted with iodine soap and cover it with a sterile drape (sheet).
- A contrast dye is injected
- Under image guidance, a small needle is inserted through the skin into the abnormal vessels, then a small amount of medication is injected through the needle into the appropriate blood vessel, which irritates the lining of the vein, causing it to swell and block the flow of blood.
- Once the needle is withdrawn, your doctor will apply compression and massage to the region to keep blood out of the injected vessel and distribute the solution.
What are the benefits VS risks?
Benefits
- Minimally invasive procedure
- Pain relief
- Enhanced appearance
Risks
The doctors will mitigate these risks as much as possible during the procedure.
- Infection
- Skin blisters
- Nerve damage (rare)
AVM Embolization
An artenovenous malformation (AVM) is an abnormal tangle of blood vessels linking arteries and veins that interferes with regular blood flow and oxygen circulation.
Why is this procedure recommended?
This procedure is recommended in the following cases:
- Before surgery or radiation to reduce hemorrhage
- High-output cardiac failure (heart failure)
- Chronic venous hypertension (increased pressure inside your veins)
- Lesions at a limb or life-threatening condition
- Disabling pain
- Functional disability
- Cosmetic deformities
How is this procedure performed?
- You will be taken into the procedure room and the anesthetist will then give you general anesthesia. You will go into deep sleep and not feel any pain.
- Your doctor will prepare the area where the needle is to be inserted with iodine soap and cover it with a sterile drape (sheet).
- A contrast dye is injected into the artery through a needle.
- Under image guidance, a small plastic tube called a catheter is introduced into the femoral artery in the upper thigh/groin area.
- From this artery, the catheter is carefully navigated into the arteries that need to be blocked.
- Special materials such as particles or glue are injected to reduce or block the flow of blood through the AVM to seal it off.
What are the benefits VS risks?
Benefits
- Minimally invasive procedure
- Faster recovery
- Relieves symptoms
Risks
- Weakness or numbness in an arm or leg
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Arterial damage at the entry site
Uterine Fibroid Embolization
What is UAE?
Uterine Artery Embolization is a procedure that shrinks noncancerous tumors in the uterus called, Uterine Fibroids, by blocking uterine arteries that supply the blood to the Fibroids.
Why is this procedure recommended?
The main reason to have a Uterine Artery Embolization is to treat the uterine tumors that cause pain or excessive bleeding.
This procedure may be recommended if you have any of the following:
- Excessive bleeding.
- Pain in your belly.
- An enlarged uterus.
- Bladder pressure that makes you feel that you need to urinate often.
- Pressure on the bowel that causes constipation and bloating.
- Pain during sexual intercourse.
How is this procedure performed?
- The procedure begins with the doctor prepping your wrist or thigh area with antiseptic solution some local anesthetic will be injected. This may sting briefly before going numb.
- The doctor will then use another needle to access a blood vessel running up your thigh or a blood vessel going up your arm.
- The doctor would then insert a small tube(sheath). This will be used as a guide to put the catheter into the blood vessel that is to be blocked.
- X-ray images or pictures are taken by a special X-ray machine after injecting X-ray contrast sometimes referred to as ‘dye. This is known as angiography and helps find the blood vessels that supply blood to the fibroids.
- Fluid containing thousands of tiny particles is then injected through the catheter into these arteries to block them. These particles do not have any side effects and cannot move into other parts of the body.
- The sheath and catheter will be removed after the embolization is done.
- The patient may be required to stay overnight
What are the benefits VS risks?
We have listed down a few benefits and risks below for better understanding
Benefits
- Non-surgical procedure
- Recovery in 1-2 weeks.
- According to research 90% of the women find relief after the surgery
- Helps avoid Hysterectomy (operation to remove the Uterus)
Risks
The doctors will mitigate these risks as much as possible during the procedure.
- Small bruise at the site of needle entry
- Mild to moderate pain, which can be relieved by painkillers
- Vaginal discharge (blood due to breakdown of fibroids)
- Chances of Infection
- Only 2% of the women pass small pieces of fibroid tissue after the procedure. In such case they may require another procedure called Dilatation & Curettage.
Breast Biopsy
Physical, mammography, and other tests often find lumps or strange things in the breast. But sometimes, it’s hard to know if these things are harmless or cancerous.
Doctors do a breast biopsy to take a small piece of tissue from the suspicious area and check it in a lab. The biopsy can be done in two ways.
- One way is with surgery, where the doctor removes the tissue.
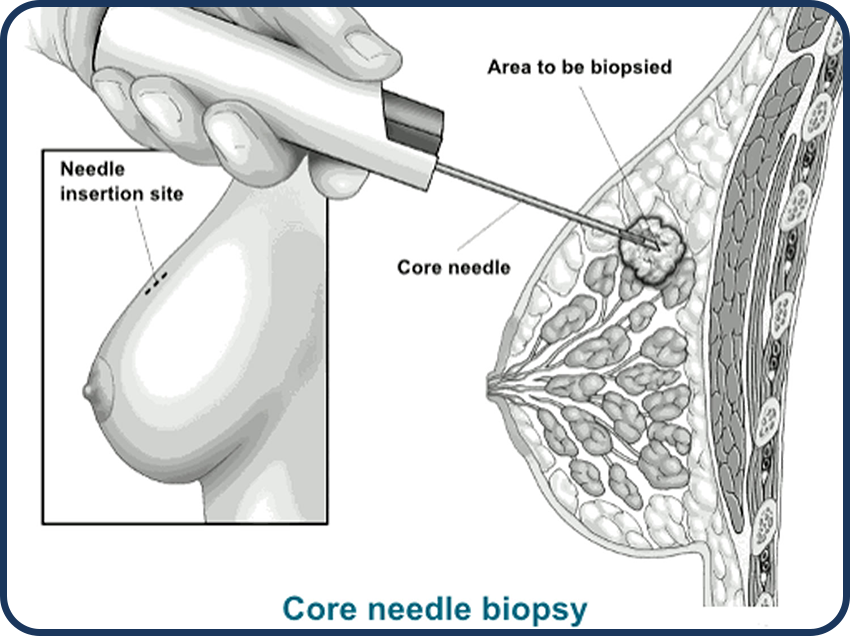
- The other way is less invasive. At PIIT our radiologist use a needle and special imaging to guide them to the area of concern. This type of biopsy doesn’t take out the whole lump. It just takes a small piece for testing.
There are different types of image-guided biopsies.
Ultrasound Guided or CT Guided Biopsy
What is FNAC (CT/US Guided)?
Why is this procedure recommended?
This procedure is usually recommended for diagnosis of the following conditions:
- Core needle biopsy
- Lung nodule or mass (Lung biopsy)
- Lump in the liver (Liver biopsy)
- Thyroid nodules (a lump that can develop in your thyroid gland)
- Breast lumps
- You have problem making blood cells (Bone marrow biopsy)
- When there is not enough access to the tumor through conventional procedure
How is this procedure performed?
The procedure begins with the doctor prepping the skin over the biopsy site with lodine soap.
- You will feel a needle stick and a brief sting as the doctor injects a local anesthetic to numb the area.
- Once the area is numb, a biopsy needle will be placed into the area through the skin and advanced to the site of nodule.
- Then, a sample will be collected (fluid or cluster of cells) using image guidance (ultrasound/CT).
- After taking the sample the interventional radiologist will confirm with the pathology department if the samples are adequate for the required evaluations.
- Once confirmed by the pathology department, only then does the IR end the procedure.
- After the procedure, the needle will be removed and firm pressure will be placed to help control any bleeding from the biopsy site.
What are the benefits VS risks?
Benefits
- Less invasive
- There is no scarring
- Higher degree of accuracy as compared to surgical biopsy
- Shorter recovery time
- Can be performed where access through conventional surgery is riskier.
Risks
- Localized bleeding or bruising
- Infection
- Damage to the structures near the area from where the sample was taken
Stereotactic Mammography Guided Breast Biopsy
A stereotactic breast biopsy is a way to check a breast problem using special x-ray pictures called mammography. It helps doctors find and take a small piece of tissue for testing. It’s not as invasive as surgery and usually doesn’t leave much scarring. This method is great for looking at calcium deposits or tiny lumps that can’t be seen on ultrasound.
Fallopian Tube Recanalization
Why is this procedure recommended?
If you’re having difficulty getting pregnant, you’re not the only one going through this.
In most developed countries about 1 in 7 couples faces fertility issues. The main reason for this is blocked fallopian tubes. These tubes are important because they let sperm meet the egg and then carry the egg to the uterus. But when they’re blocked, this can’t happen, making it hard to get pregnant.
Fallopian tube recanalization is a simple procedure to reopen these blocked tubes. It works well for about 8 to 9 out of 10 women who have it done. And half of those women will end up having a baby.
How is this procedure performed?
During the procedure, some women might feel cramping, so the doctor might offer them medicine to help feel better.
- First, the doctor will use a tool called a speculum, which is like what they use during a Pap smear, to gently open the vagina. Then, they will insert a very tiny tube through the vagina and into the uterus. They inject some dye through this tube and using low dose x-ray image guidance they can see if the fallopian tubes are blocked.
- If they find that one of the fallopian tubes is blocked, the doctor will pass a small wire through the tube to clear the blockage. The whole procedure usually lasts between 15 to 30 minutes.
Gonadal Vein Embolization
Why is this procedure recommended?
Pelvic congestion syndrome (PCS) is a condition that causes ongoing pelvic pain in women. This pain gets worse when standing or sitting for long periods and can also make intercourse painful.
PCS happens when blood backs up and gathers in the veins of the pelvis, making them stretch. These swollen veins can also show up in the thighs, buttocks, or vaginal area, resembling varicose veins in the legs.
At PIIT a minimally invasive procedure called “gonadal vein embolization ” is performed under Image guidance. This procedure blocks the problematic veins from the inside, reducing pressure and relieving most or all of the PCS symptoms in about 8 to 9 out of 10 women.
How is this procedure performed?
- To start, you’ll receive medications to help you relax during the procedure. The clinician will then numb the skin on your neck or upper thigh.
- Next, they’ll carefully insert a thin tube through the skin into a large vein. Using real time x-rays images as a guide, the clinician will navigate the small tube into the unhealthy veins in your pelvis.
- Once in place, the clinician will inject special material into these unhealthy veins to block them and redirect blood flow through your healthy veins. Afterward, the tube will be removed, and a dressing will be placed over the insertion site on your skin.

